Often partial differential equations can be reduced to a simpler form with a solution known as the corresponding change of variable .
This article discusses the variable changes for PDEs below in two ways:
- with an example;
- by giving the method theory.
Video Change of variables (PDE)
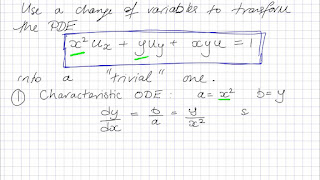
Description with example
Misalnya, bentuk yang disederhanakan dari PDE Black-Scholes
-
direduksi menjadi persamaan panas
-
oleh perubahan variabel:
-
-
-
-
Suggestions on applying change of variables for PDEs are given by mathematician J. Michael Steele:
Misalkan kita memiliki fungsi dan perubahan variabel sehingga ada fungsi seperti itu
-
-
dan fungsi seperti itu
-
-
dan selanjutnya seperti itu
-
-
dan
-
-
In other words, it would be helpful to be the ore between a set of old and new variables, or else it should be
- Limit the domain of applying correspondence to the subject of a real field sufficient for handling practical problem solutions (where else needs to be grained), and
- Mention (zero or more limited list) of (polar) exceptions where the opposite-bijection fails (and tell me why this exception does not restrict the application of the solution from the equation reduced to the original equation)
If an ore does not exist then the solution to the reduced-form equation will not generally be the solution of the original equation.
Kami sedang mendiskusikan perubahan variabel untuk PDE. PDE dapat dinyatakan sebagai operator diferensial yang diterapkan ke suatu fungsi. Misalkan adalah operator diferensial seperti itu
-
Maka itu juga yang terjadi
-
dimana
-
Seringkali, teori dapat menetapkan adanya perubahan variabel, meskipun rumus itu sendiri tidak dapat secara eksplisit dinyatakan. Untuk sistem dimensi Hamiltonian terintegrasi , dengan dan , terdapat integral . Terdapat perubahan variabel dari koordinat
Source of the article : Wikipedia

